Aim:
To Write a C Program to Implement Singly Linked List.
Theory:
A linked list is a way to store a collection of elements. Like an array these can be character or integers. Each element in a linked list is stored in the form of a node.
Node:
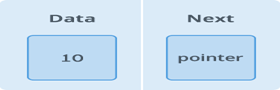
A node is a collection of two sub-elements or parts. A data part that stores the element and a next part that stores the link to the next node.
Linked List:

A linked list is formed when many such nodes are linked together to form a chain. Each node points to the next node present in the order. The first node is always used as a reference to traverse the list and is called HEAD. The last node points to NULL.
Why Linked List?
Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have following limitations.
- The size of the arrays is fixed: So we must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to the upper limit irrespective of the usage.
- Inserting a new element in an array of elements is expensive; because room has to be created for the new elements and to create room existing elements have to shift.
For example, in a system if we maintain a sorted list of IDs in an array id []. id [] = [1000, 1010, 1050, 2000, 2040].
And if we want to insert a new ID 1005, then to maintain the sorted order, we have to move all the elements after 1000 (excluding 1000).
Deletion is also expensive with arrays until unless some special techniques are used. For example, to delete 1010 in id[], everything after 1010 has to be moved.
Advantages over arrays
- Dynamic size
- Ease of insertion/deletion
Drawbacks:
- Random access is not allowed. We have to access elements sequentially starting from the first node. So we cannot do binary search with linked lists efficiently with its default implementation.
- Extra memory space for a pointer is required with each element of the list.
- Not cache friendly. Since array elements are contiguous locations, there is locality of reference which is not there in case of linked lists.
Representation:
A linked list is represented by a pointer to the first node of the linked list. The first node is called head. If the linked list is empty, then value of head is NULL.
Each node in a list consists of at least two parts:
- data
- Pointer (Or Reference) to the next node
In C, we can represent a node using structures. Below is an example of a linked list node with an integer data.
Algorithm:
- Create a structure with an element (Element) and a pointer (Next) that points to the next node in the list.
- Create a head pointer using the malloc function and assign the resultant pointer variable to the head pointer S.
- In the Push operation, create a new node, called TmpCell using the malloc function, assign the new element X to TmpCell->Element, make TmpCell point to the node that was previously pointed to by the head pointer and make the head pointer point to TmpCell by the statements: TmpCell->Next=S->Next and S->Next=TmpCell.
- In the Pop operation, store the node pointed to by the head pointer in a pointer called FirstCell by the statement FirstCell=S->Next. Then make the head pointer point to the node next to FirstCell by the statement S->Next=S->Next->Next. Then free FirstCell.
- In the Top operation, return the element pointed to by the head pointers next node by the statement S->Next-> Element.
Program:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int c=0;
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *temp,*head=NULL,*newnode,*new1;
void insert()
{
int x;
newnode=(struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf ("\nENTER THE VALUE: ");
scanf ( "%d",&x);
printf("%d",x);
if(head==NULL)
{
newnode->data=x;
head=newnode;
new1= head;
temp=newnode;
}
else
{
newnode->data=x;
temp->next=newnode;
temp=newnode;
newnode->next=NULL;
}
c++;
}
void delet()
{
if(head==0)
{
printf("EMPTY");
}
else
{
printf("\nNO DELETE IS %d\n",head->data);
head=head->next;
new1=head;
c--;
}
}
void display ()
{
printf("\nLINKED LIST\n");
while(new1!=NULL)
{
printf ("%d\n",new1->data);
new1=new1->next;
}
new1=head;
}
void insertF()
{
struct node*newnode;
newnode=(struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf("ENTER THE VALUE: ");
int a;
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("%d\n",a);
newnode->data=a;
newnode->next=head;
new1=head=newnode;
c++;
}
void insertS()
{
if(head==0)
{
printf("EMPTY");
}
else
{
struct node*newnode;
newnode=(struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node*temp3=head;
printf("\nENTER THE POSITION : ");
int i;
scanf("%d",&i);
printf("%d",i);
int j=1;
for(j=1;j<i-1;j++)
{
temp3=temp3->next;
}
printf("ENTER THE VAL: ");
int a;
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("%d\n",a);
newnode->data=a;
newnode->next=temp3->next;
temp3->next=newnode;
c++;
}
}
void deletel()
{
if(head==0)
{
printf("\nEMPTY\n");
}
else{
struct node*temp4=head;
int i;
for(i=1;i<c-1;i++)
{
temp4=temp4->next;
}
temp4->next=0;
free(temp);
temp=temp4;
new1=head;
c--;
}
}
void delsp()
{
struct node *temp5=head,*temp6=head;
if(head==0)
{
printf("\nEMPTY\n");
}
else {
printf("\nENTER THE POSITION: ");
int pos;
scanf("%d",&pos);
printf ("%d\n",pos);
int i;
for(i=1;i<pos;i++)
{
temp6=temp6->next;
}
for( i=1;i<pos-1;i++)
{
temp5=temp5->next;
}
temp5->next=temp6->next;
c--;
}
}
int ex()
{
printf(" \nI M EXITING ");
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int ch,i=0;
while(i<1)
{
printf("\nMAIN MENU\n\n1.INSERT\n2.DELETE\n3.DISPLAY\n4.INSERT FIRST\n5.INSERT SPECFIC\n6.DELETE LAST\n7.DELETE SPECIFIC\n8.EXIT\n");
scanf("%d",&ch);
printf("YOUR CHOICE IS: %d",ch);
switch (ch)
{
case 1:
insert();
break;
case 2:
delet();
break;
case 3:
display();
break;
case 4:
insertF();
break;
case 5:
insertS();
break;
case 6:
deletel();
break;
case 7:
delsp();
break;
case 8:
i=ex();
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
Execution:
Input: 1 45 1 32 1 67 2 3 4 56 5 2 67 6 7 2 8 Output: MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 1 ENTER THE VALUE: 45 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 1 ENTER THE VALUE: 32 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 1 ENTER THE VALUE: 67 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 2 NO DELETE IS 45 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 3 LINKED LIST 32 67 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 4ENTER THE VALUE: 56 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 5 ENTER THE POSITION : 2ENTER THE VAL: 67 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 6 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 7 ENTER THE POSITION: 2 MAIN MENU 1.INSERT 2.DELETE 3.DISPLAY 4.INSERT FIRST 5.INSERT SPECFIC 6.DELETE LAST 7.DELETE SPECIFIC 8.EXIT YOUR CHOICE IS: 8 I M EXITING
Result:
Thus, Implement single linked list was executed successfully.
