stat():
This function return information about a file.
a stat structure, which contains the following fields:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
};
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The following example shows how to use stat system call in C programming language in Linux, Ubuntu.
EXAMPLE 1:{ref: https://linuxhint.com/stat-system-call-linux/}
In the following code we are going to find the mode of a file:
Program:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
struct stat sfile; //pointer to stat struct
stat("stat.c", &sfile); //stat system call
printf("st_mode = %o", sfile.st_mode); //accessing st_mode (data member of stat struct)
return 0;
}
Output:
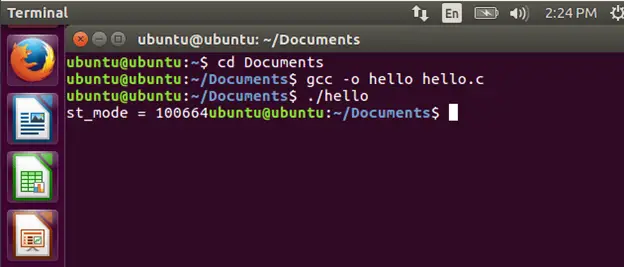
- In this code, we have passed the name of the file in the stat system call and then the pointer to stat struct which is sfile.
- The pointer to stat struct is then used to access st_mode which displays the mode of the file using printf statement.
- The header file <sys/stat.h> is used so you can use a stat system call.
- The header file <stdio.h> is the standard input/output library file so that you can use printf or scanf in your C code.
