Aim:
To write a C++ program for array implementation of List ADT.
Description:
- A linked list is a sequence of data structures, which are connected together via links.
- Linked List is a sequence of links which contains items. Each link contains a connection to another link.
- Linked list is the second most-used data structure after array.
- Following are the important terms to understand the concept of Linked List.
- Link − each link of a linked list can store a data called an element.
- Next − each link of a linked list contains a link to the next link called Next.
- Linked List − A Linked List contains the connection link to the first link called First.
Algorithm:
- Step 1: Create nodes first, last; next, prev and cur then set the value as NULL.
- Step 2: Read the list operation type.
- Step 3: If operation type is create then process the following steps.
- Allocate memory for node cur.
- Read data in cur’s data area.
- Assign cur node as NULL.
- Assign first=last=cur.
- Step 4: If operation type is Insert then process the following steps.
- Allocate memory for node cur.
- Read data in cur’s data area.
- Read the position the Data to be insert.
- Availability of the position is true then assing cur’s node as first and first=cur.
- If availability of position is false then do following steps.
- Assign next as cur and count as zero.
- Repeat the following steps until count less than postion.
- Assign prev as next
- Next as prev of node.
- Add count by one.
- If prev as NULL then display the message INVALID POSITION.
- If prev not qual to NULL then do the following steps.
- Assign cur’s node as prev’s node.
- Assign prev’s node as cur.
- Step5: If operation type is delete then do the following steps.
- Read the position .
- Check list is Empty .If it is true display the message List empty.
- If position is first.
- Assign cur as first.
- Assign First as first of node.
- Reallocate the cur from memory.
- If position is last.
- Move the current node to prev.
- cur’s node as Null.
- Reallocate the Last from memory.
- Assign last as cur.
- If position is enter Mediate.
- Move the cur to required postion.
- Move the Previous to cur’s previous position
- Move the Next to cur’s Next position.
- Now Assign previous of node as next.
- Reallocate the cur from memory.
- Step 6: If operation is traverse.
- Assign current as first.
- Repeat the following steps untill cur becomes NULL
Program:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<process.h>
void create();
void insert();
void deletion();
void search();
void display();
int a,b[20],n,d,e,f,i;
void main()
{
int c;
clrscr();
cout<<"\n Main Menu";
cout<<"\n 1.Create \n 2.Delete \n 3.Search \n 4.insert \n
5.Display \n 6.Exit";
do
{
cout<<"\n enter your choice:";
cin>>c;
switch(c)
{
case 1: create(); break;
case 2: deletion(); break;
case 3: search(); break;
case 4: insert(); break;
case 5: display(); break;
case 6: exit(0); break;
default:
cout<<"The given number is not between 1-5\n";
}
}
while(c<=6);
getch();
}
void create()
{
cout<<"\n Enter the number of elements you want to
create: "; cin>>n;
cout<<"\nenter the elements\n";
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>b[i];
}
}
void deletion()
{
cout<<"Enter the number u want to delete \n";
cin>>d;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(b[i]==d)
{
b[i]=0;
cout<<d<<" deleted";
}
}
}
void search()
{
cout<<"Enter the number \n";
cin>>e;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(b[i]==e)
{
cout<<"Value found the position\n"<<i+1;
}
}
}
void insert()
{
cout<<"\nenter how many number u want to insert: ";
cin>>f;
cout<<"\nEnter the elements\n";
for(i=0;i<f;i++)
{
cin>>b[n++];
}
}
void display()
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<"\n"<<b[i];
}
}
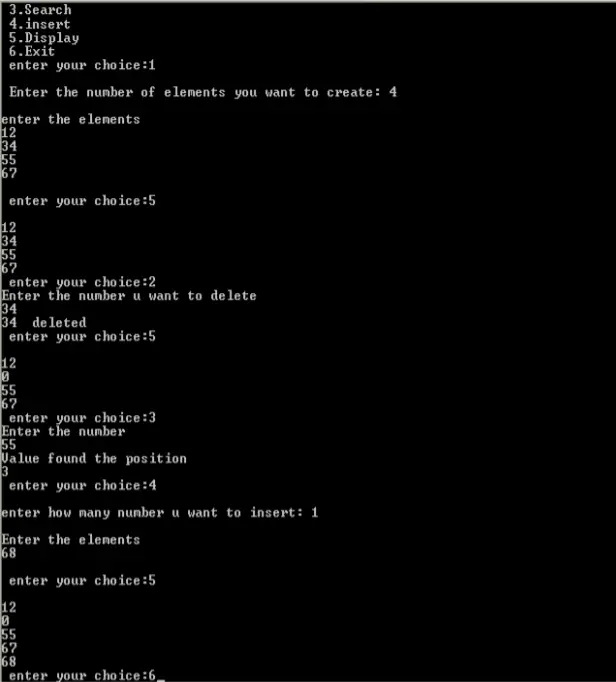
Output:
Result:
Thus the C++ program for array implementation of list ADT was created, executed and output was verified successfully